How to use Google Classroom like a Pro - A Guide for Teachers
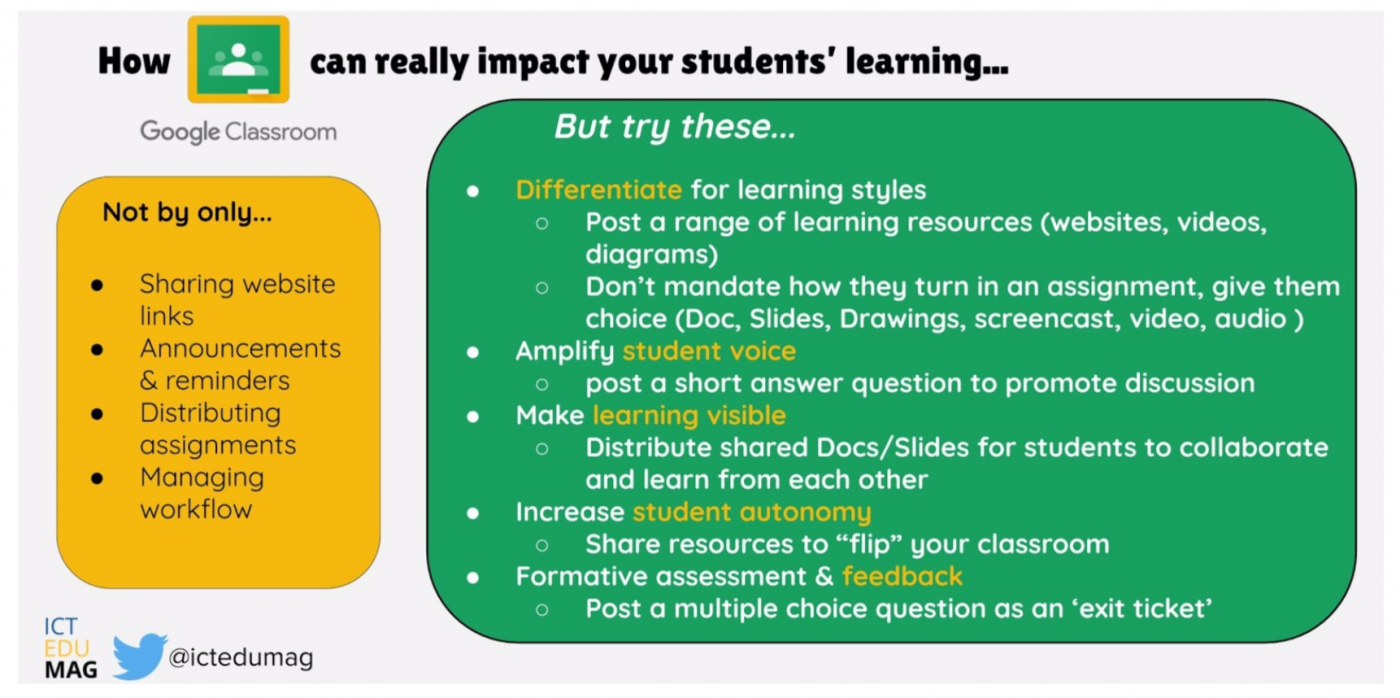
/One of the most universally used tools in schools is without a doubt, Google Classroom. Whilst many teachers are drawn to its ease of use to post announcements, share links and manage workflow, there is a deeper level in which Classroom can be used to enhance learning and teaching. How many of the following have you tried?
Increase Student Autonomy
By simply posting your own screen casts or ready made ones (Khan Academy etc.), you can empower students to learn at their own pace. Small groups can be using the digital resource while you teach face to face with another group.
HINT: post on the Classwork tab as a ‘Material’ under the relevant topic to ensure the video is easy to access. Not everything has to be an ‘Assignment’ if there isn’t anything to ‘turn in’.
Differentiate for Learning Styles
When posting an assignment, allow students to ‘Add’ evidence of their learning in whatever format they choose (within reason!) – images, videos, voice recording, screen cast, Doc, or Slides. This element of choice is not only engaging for students, it caters for different learning styles.
Make Learning Visible
Use Classroom to share out a single Doc or Slides presentation that each student can edit. This collaborative approach to learning allows students to see and learn from their peers. It not only supports weaker students by scaffolding their learning, but it provides an audience for student writing.
HUGE COLLECTION OF GOOGLE CLASSROOM GRAPHIC ORGANIZERS
Perfect tool for critical and creative thinking
Works seamlessly with Google Classroom
Covers all curriculum areas
Fully Editable
Make Learning Visible
Use Classroom to share out a single Doc or Slides presentation that each student can edit. This collaborative approach to learning allows students to see and learn from their peers. It not only supports weaker students by scaffolding their learning, but it provides an audience for student writing.
I like to also share my expectations about writing in a shared Doc – Golden Rules of Team Writing.
Amplify Student Voice
Pose a short answer question (ensure it?s open ended) and students reply with their opinion.
Importantly, don’t stop the lesson there. Encourage students to then read each other’s responses and leave comments.
Use the ‘Guide to Commenting’ to help scaffold appropriate digital commenting.
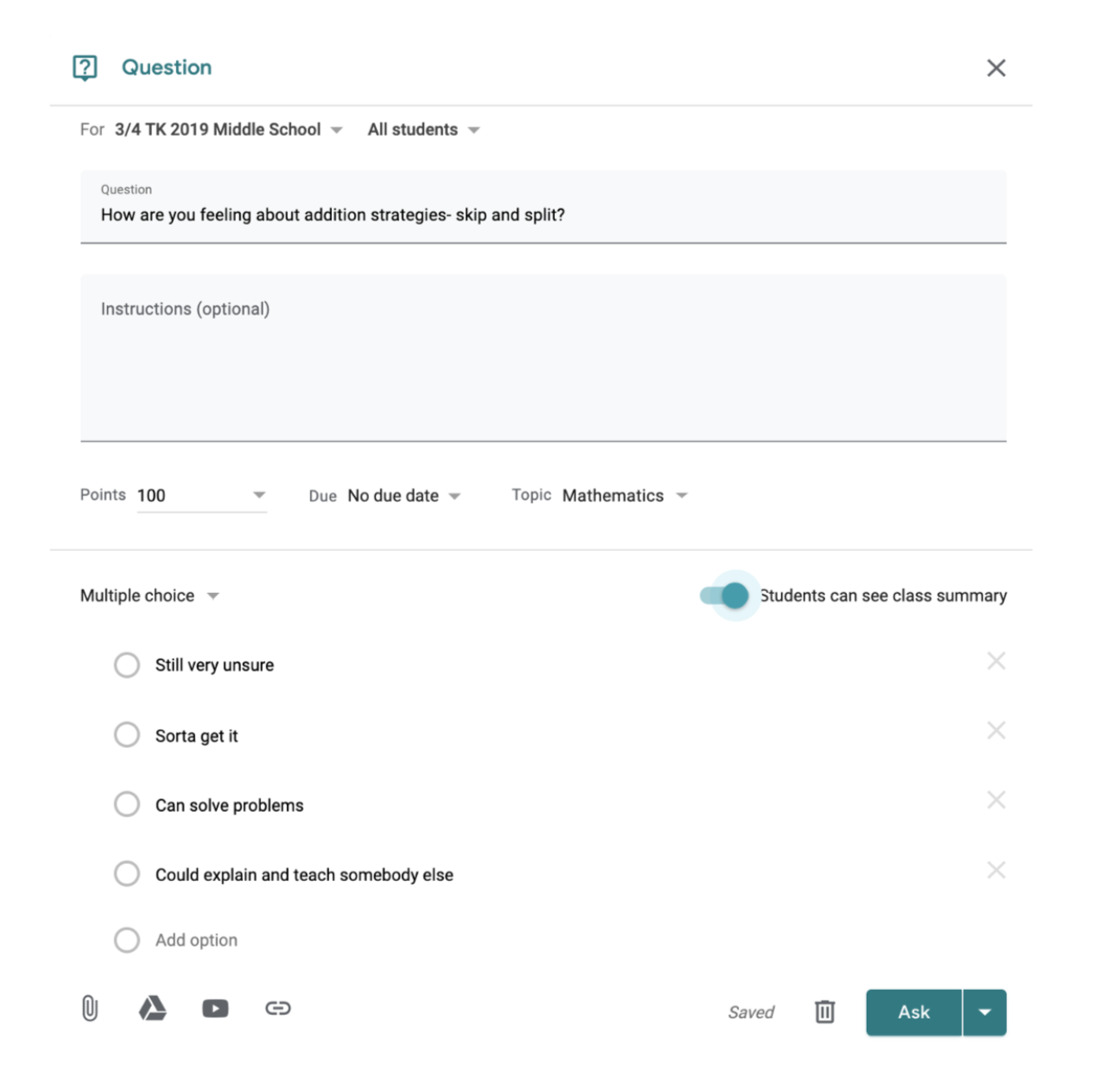
Formative Assessment and Feedback
A super simple but very powerful use of Classroom is to post an ‘exit ticket’ for students to complete. You, as the teacher, can get a clear insight into how students are progressing with their learning.
Other ideas for exit tickets:
3 things you learnt
1 question you still have
specific content related multiple choice question